Sliding Window’s method
- push all data into a 0.1×0.1×0.1 $m^3$ per cell
- sub item one
- sub item two
- sub item three
- sort cells from high to low
- use sliding window with hight threshold
- compute height difference of this cell
- also consider neighbour cells
plane point ransac filter
- choose approximate ground data
- use PCL’s ransac segmentation model
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients (new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers (new pcl::PointIndices);
// Create the segmentation object
pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg;
// Optional
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients (true);
// Mandatory
seg.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);
seg.setMethodType (pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setDistanceThreshold (0.01);
seg.setInputCloud (cloud);
seg.segment (*inliers, *coefficients);
tricks 1
for one frame lidar data, we may choose the downside lidar(the red curve), this will save a lot of time.
tricks 2
seg.setDistanceThreshold( 0.05 );
seg.setAxis( axis );
seg.setEpsAngle( pcl::deg2rad( 10.0 ) );
the plane may vertical to vector(0,0,1), so we’d better to set axix to be (0,0,1) as well as the Eps angle.
tricks 3
what if we may encounter two planes, like this:
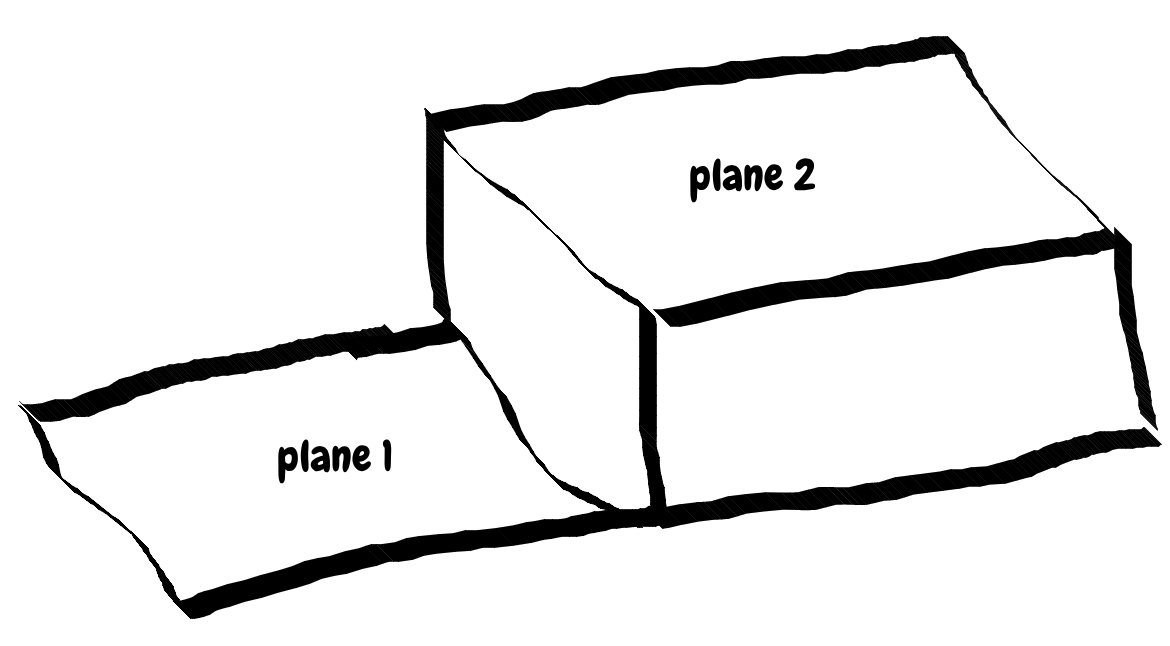
and if this time it’s not good we may seg it again(with last time’s coeef),Its interface is like this:
void seg_ground_cloud( pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr& coefficients,
Eigen::Vector3f& axis,
int threshold = 0.05 );
plane point angle_method1
we have one frame data like this:
 for every column,data like this:
for every column,data like this:
 we use this stratege, like this:
we use this stratege, like this:
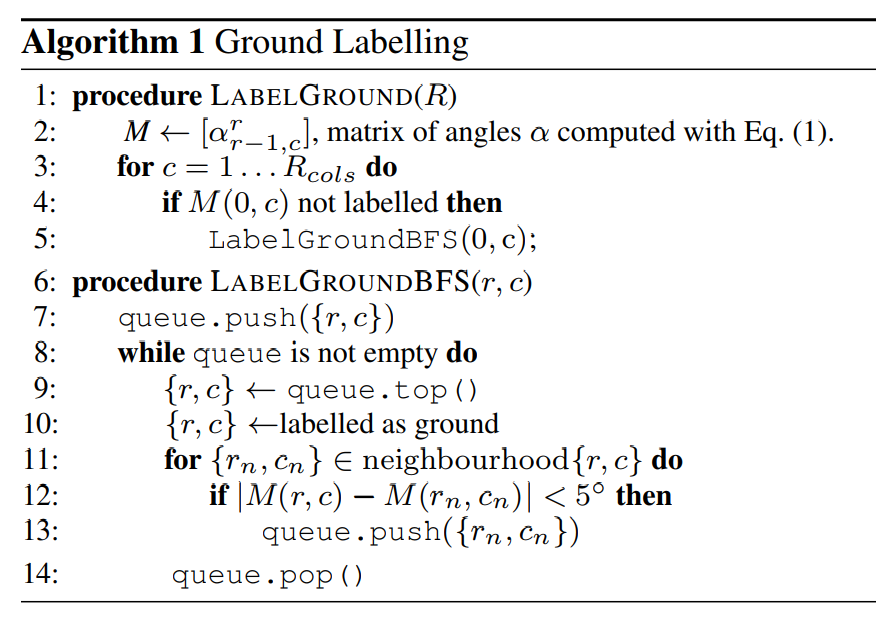
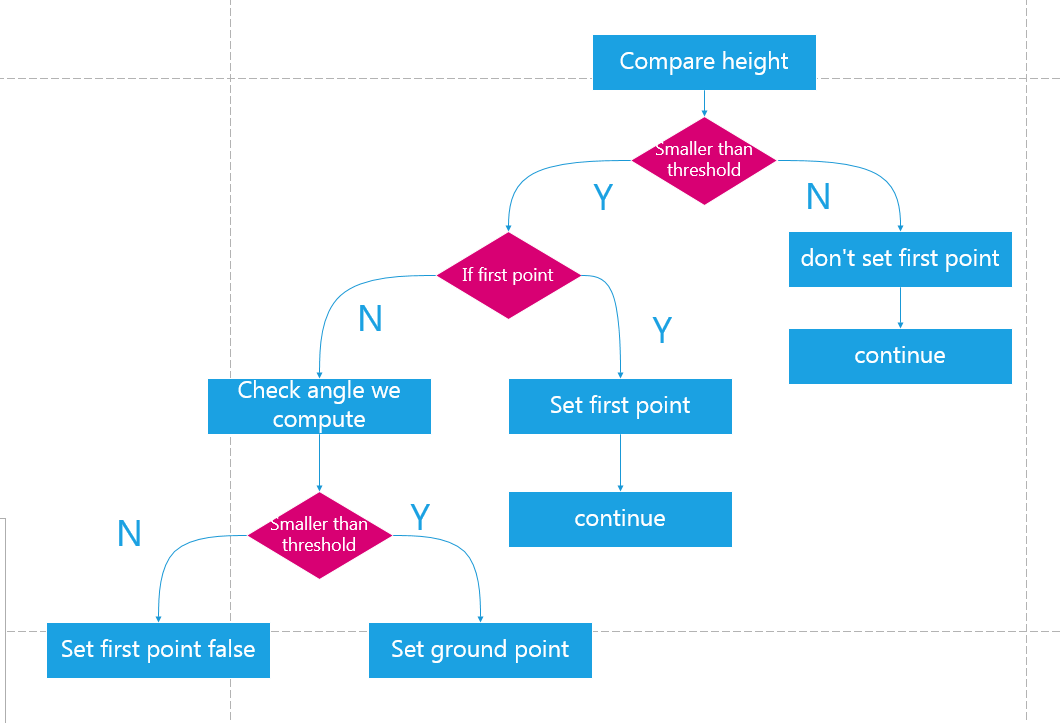
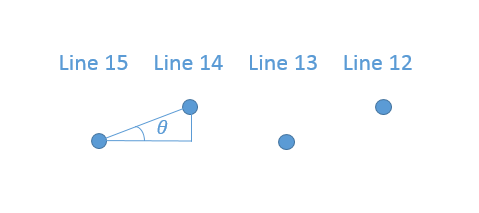 if the angle we get is above threshold, we think it’s not ground point, and cotinue.And main precedure is under below:
if the angle we get is above threshold, we think it’s not ground point, and cotinue.And main precedure is under below:
plane point angle_method1
main difference: not only consider vertical angle, but also horizontal angle .The author use BFS method to compute which are ground points, the algorithm is like this: